InDirect / Reported Speech | Rules:
- Rules of Say
- Rule of That
- Rules of Words
- Rules of Pronoun
- Rules of Pronoun Replacement
1) Rules Of - "Say"
Rules of Say | Explanation:
Say - Will Be Changed To - Say
Say to - Will Be Changed To - Tell
Said - Will Be Changed To - Said
2) Rule of - "That"
Whenever we will have a ( , " ) - Comma and quotation mark | in our sentence we replace it with the word "That" . The picture above is showing you exactly what i am saying
3) Rule of Pronoun:
| Subject | Object |
|---|---|
| I | me |
| We | Us |
| You | You |
| He | him |
| She | her |
| They | them |
4) Rule Of - "Words"
The rule of words is that whenever we will have left side word in our sentence then we will replace it with right side word For Example: "Today" this word will changed into " That day " below is the list of all the words
Today -- Will Be Changed To -- That Day
Tomorrow -- Will Be Changed To -- The next day
Last Monday -- Will Be Changed To -- The Previous Monday
This/These -- Will Be Changed To -- That/These
Now -- Will Be Changed To -- Then
5) Pronoun Replacement
This rule is very important and it has three (3) conditions.Condition No - 1 If in our sentence we have (I, We) After [, "] - Comma and quotation mark then we will get the Subject As you can see below. after [, "] - Comma and quotation mark we have (I) therefore we are taking the subject Which is "He" and replacing (He With I)
Condition No - 2 If we have You After , " - Comma and quotation mark then we will get the object (means the last word before [, "] - Comma and quotation mark) but you must be saying ok i got it but this picture is showing totally opposite of what you saying because if we take the last word then i would be (Me not I) right!!! yes you are right but if you see the third rule you will find whenever we will have me then we will replace that me with I . so as i have done i had The word (Me) at the end but i changed it with (I)
Condition No - 3 If we have He,She,it,they After , " - Comma and quotation mark then we will get nothing. For Instance: He said to me ,"She Likes Apples" - As you can see After [, "] - Comma and quotation mark we have the word (She) so its means we will not anything and then our sentence will become - (He told me that She Likes Apples) so did not get anything. your confusion will be more clear after seeing the proper making process which is down below
- If (I,we) --- Get A Subject
- If (You) --- Get An Object
- If (He,She,it,they) --- No Change
How To Make - Examples?
Now We are going to learn how to make Sentence But Before we move forward i want to tell you that Whenever you will start making sentences first you will have the Sentence of direct / reporting speech available like this One ->(' She says to me , "I Teach English" ') now your work will be make example using below steps and please don't be confuse because everything will be clear after you see the given steps
Sentence : She says to me , "I Teach English"
- Step No 1 - First we will take the - She
- Step No 2 - Second we will take the - says to but before we take this we have to see in Rule of Say and in the rules we will see what is the change of says to and the change is tells
- So till now our indirect sentence is She tells
- Step No 3 - Third we will take me so then sentence will become - She tells me
- Step No 4 - Fourth We will replace ( " , ) Comma and quotation mark With That
- Now our sentence is She tells me that
- Step No 5 - Fifth we will see after comma what we have means do we have I , we Or Your because in this case we have I so will take the subject which is she don't be confuse this is from Rule No 5
- Now we the sentence is She tells me that she
- Step No 6 - we will take teach but because we are learning present narrations and as you know in present we have the rule of third person singular which means we have she so will add es at the end of the verb and in this example verb is teach so it will become teaches
- Now we have successfully made our sentence Which is (She tells me that she teaches English)
Normal
Example
|
Change
Into Direct / InDirect
|
1 - She says to me , "I Teach
English"
|
She tells me That she Teaches
English
|
2 - They say to us , "We
learn Computer"
|
They tell us that They learn
Computer
|
3 - He says to me , "I play
football"
|
He says to me That he plays
football
|
I hope now its clear how to make sentences but this is a very simple way means we can also make sentences in (Modals, Wh-Words , Imperative Sentences , Universal Truth). to teach how to make examples in (Modals, Wh-Words , Imperative Sentences , Universal Truth) below i have given their usage , structure so that you not only learn how the basics but understand each and ever
Wh-Words - In Reported Speech:
Definition:
We use Wh-Words for asking QuestionsRules:
- Said To --- Ask
- Question changes into Statement
- That --- If /Whether
Rules Explanation:
1) Said To --- Ask - [ He said to me --- Will be changed to --- He asked me If ]
3) That --- If /Whether - [ They said to us , "Do We learn Computer"? --- Will be changed to --- They asked us If They learnt Computer ]
Examples
Normal
|
WH-Words
|
1 - He said
to me, "Are you a Teacher"?
|
He asked me
If He was a Teacher
|
2 - They said to us,
"Do We learn Computer"?
|
They asked us If
They learnt Computer
|
3 - He said to me,
"Do I play football"?
|
He asked me If he
played football
|
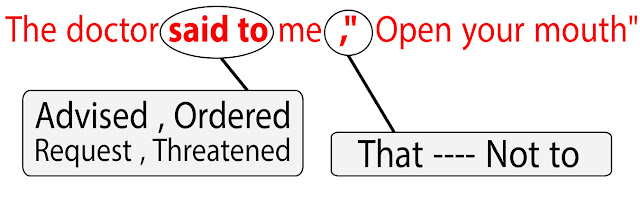
Imperative - Sentences
Rules:
- Said To --- Advised , Ordered , Request , Threatened [ According to Situation ]
- That ---- Not to
Examples
Normal
|
Imperative
|
1 - The doctor said
to me, "Open your mouth"
|
The doctor ordered
me to open my mouth
|
2 - The police said
to him ,"Don't park your car here"
|
The police Ordered
him not to park his car there
|
3 - He said To us ,
"Do not do cheating in exams"
|
He ordered us not to
do cheating in exams
|
Modals - Direct InDirect:
- Can ---- We Use Can To Show - [ Ability , Request , Permission , Possibility ] and if you want to learn can in detail so kindly visit this Can Modal Page
- Will ---- Will is the helping verb of future indefinite tense
- Shall ---- Shall is also the helping verb of future indefinite but the only difference is that we use Shall only with ( I , We )
- Must ---- We Use Must To Show - [ Personal Feeling , Certainty of Work , Importance of Work ]
- May ---- [ Permission , Possibility , Pray ]
So these are the modals which we can use in our narrations and more over if you don't understand any of modal here no need to take tension because i have already made the detail explanation on each modals. if its hard for you to find any of these modals in my website again no tension because i have given the links to particular pages which you can see above
Rules For Modals:
- Can ---- Could
- Will ---- Would
- Shall ---- Should
- Must ---- Had To
- May ---- Might
Examples
Normal
|
Modal
|
1 - He said to,
"You can teach English"
|
He told me that I
could teach English
|
2 - They said to us
, "We can speak Punjabi"
|
They told us that
They Could speak Punjabi
|
3 - He said ,
"I can play football"
|
He said that he
Could play football
|
Universal Truth - InDirect - Reported Speech:
Example: He said , "Sun rises from the east" - So in this example " Sun rises from the east "Means which we can not change because we can't say in narrations that sun rises from the west or anything because this is the truth
One more example i can give you let say someone said you that " every one has to die " if you see this so it's universal truth because no one can change this truth. this is Universal Truth In Direct InDirect
| Normal | Universal Truths |
|---|---|
| 1 - He said , "Sun rises from the east" | He said that Sun rises from the east |
| 2 - They said , "Heart pumps blood" | They said that Heart pumps blood |
| 3 - She said , "Mumbai is the biggest city of India " | She said that Mumbai is the biggest city of India |
Narration (Direct-Indirect) Examples
For example -- He says, "I take coffee". (Direct)
He says that he takes coffee. (Indirect) - He is saying, "I was suffering from fever". (Direct)
He is saying that he was suffering from fever. (Indirect) - My friend said, "I am fine".
My friend said that he was fine. - She said to me, "You are right".
She told me that I was right. - Mohan said, "I am doing work".
Mohan said that he was doing work. - Radha said, "I have finished her work".
Radha said that she had finished her work. - You said to me, "I went to Mumbai".
You told me that you had gone to Mumbai. - He said, "The bus had left".
He said that the bus had left. - He said, "I shall bring your book tomorrow".
He said that he would bring my book the next day. - The teacher said to me, "The boy will go on a picnic".
The teacher told me that the boy would go on a picnic. - He said, "Man is mortal".
He said that man is mortal. - You say, "I am doing work".
You say that you are doing work. - I say to him, "You cannot win the match".
I tell him that he cannot win the match. - They say to me, "We shall help you".
They tell me that they will help me. - She says to me, "I did not break you pen".
She tells me that she did not break my pen.
Rule I- Connective word 'that' is not used in the indirect speech.
Rule II- Reporting verb is changed into 'ask' or 'asked' in the indirect speech.
Rule III - Mark of interrogation (?) is removed in the indirect speech.
For example-
- He said to me, "Are you studying?"
He asked me if I was studying. - He said to me, "Have you done your work?"
He asked me if I had done my work. - She said to me, "Do you take tea?"
She asked me if I took tea. - He said to me, "Did you take lunch?"
He asked me if I had taken lunch. - She said to me, "Can you do it?"
She asked me if I could do it. - He said to me, "What are you doing?"
He asked me what I was doing. - She said to me, “How old are you?"
She asked me how old I was. - He said to me, "Why do you play cricket?"
He asked me why 1 played cricket. - She said to me, "Where do you come from?"
She asked me where I came from. - I said to Ram, "Which is your pen?"
I asked Ram which his pen was.
Rule - I:- Reporting verb is changed into asked ordered, requested, advised, proposed, suggested or forbade etc.
Rule - II:- Connective word 'that' is not used.
Rule - III:- 'To' is used before the verb of the reported speech.
For example-
- He said to the servant, "Open the door".
He ordered the servant to open the door. - My father said to me, "Study hard".
My father advised me to study hard. - He said to me, "Please give me your pen".
He requested me to give him my pen. - I said to him, "Let me do it".
I requested him to let me do it. - I said, "Let me speak first".
I requested to let me speak first.
Type - IV (Exclamatory and Optative Sentences)
Rule I: - Reporting verb is changed into -exclaimed with joy or with sorrow or with surprise, applauded, wished, prayed etc.
Rule II- Words of exclamations, i.e., Hurrah, alas, ah, Oh! Etc. are removed.
Rule III- Mark of exclamation (!) is removed.
Rule IV- Connective word 'that' is used.
For example-
- He said, "Alas! I am ruined."
He exclaimed with sorrow that he was ruined. - My friend said, "Hurrah! I have won the match."
My friend exclaimed with joy that he had won the match. - She said, "What a beautiful scenery!"
She exclaimed with surprise that it was a very beautiful scenery. - The Caption said, "Bravo! Well done."
The Caption applauded saying that they had done well. - He said, "Good morning, boys!"
He wished good morning to boys.